Understanding & Coping with Postpartum Depression | Kienthucsannhi.com. In today’s article, kienthucsannhi.com will explore with you in the most detailed and complete way. See now!
Understanding Postpartum Depression
What is Postpartum Depression?
Postpartum depression (PPD) is a serious mental health condition that can affect women after childbirth. It’s not just the “baby blues,” a temporary phase of mood swings and fatigue. PPD is characterized by persistent sadness, anxiety, and feelings of inadequacy that can significantly interfere with daily life. Unlike the “baby blues” which typically fade within a few days, PPD can last for weeks, months, or even years if left untreated.
Symptoms of Postpartum Depression
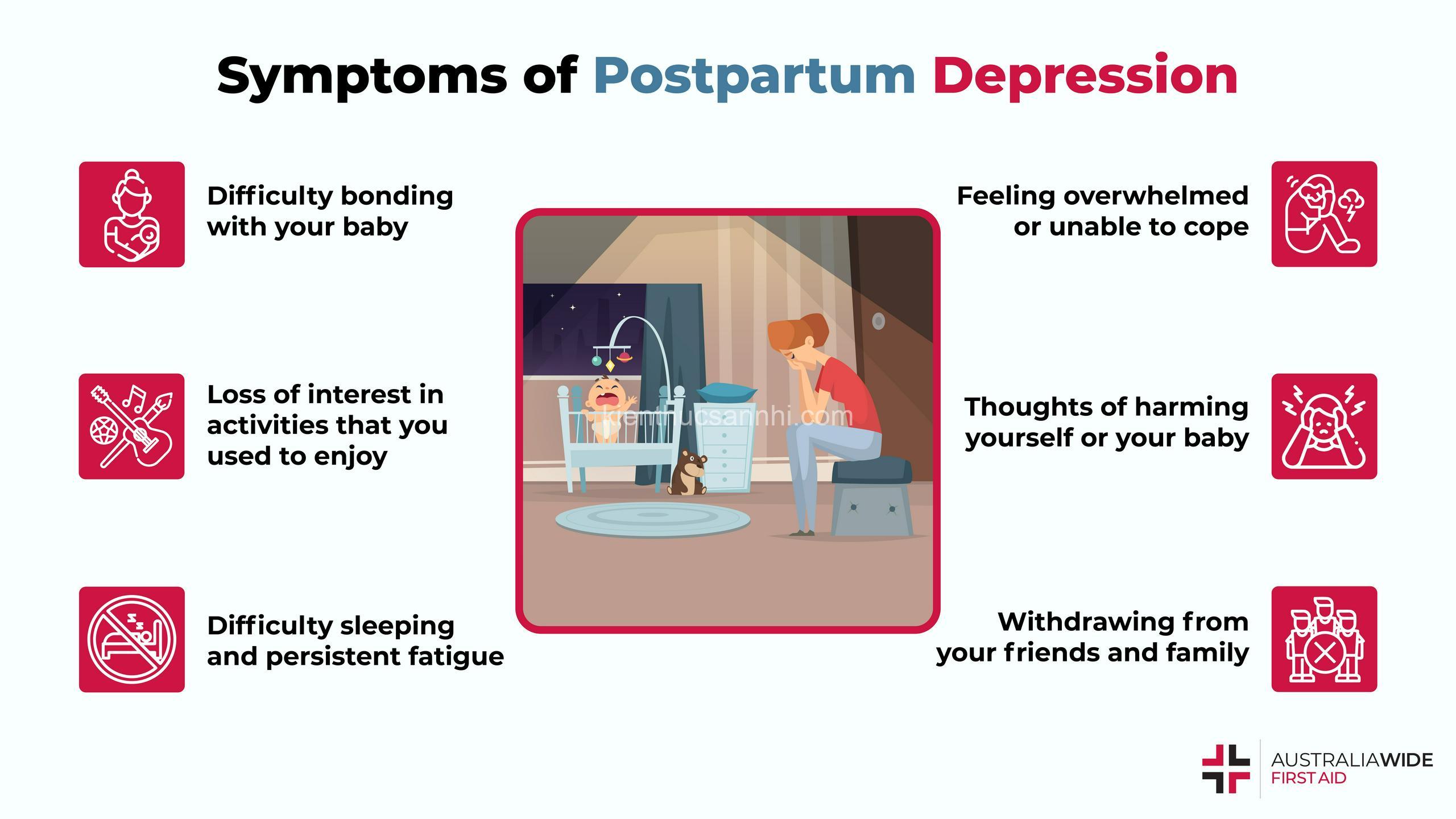
Postpartum depression can manifest in various ways. Some common symptoms include:
- Emotional Symptoms:
- Feeling overwhelming sadness, hopelessness, or emptiness
- Feeling anxious, irritable, or restless
- Difficulty bonding with your baby
- Loss of interest in activities you once enjoyed
- Feeling overwhelmed or inadequate as a parent
- Thoughts of harming yourself or your baby (seek immediate help if you have these thoughts)
- Physical Symptoms:
- Fatigue or lack of energy
- Changes in appetite, either eating too much or too little
- Difficulty sleeping, either sleeping too much or too little
- Physical aches and pains
- Behavioral Symptoms:
- Withdrawing from family and friends
- Neglecting personal hygiene
- Difficulty concentrating or making decisions
- Engaging in risky behaviors
Causes of Postpartum Depression
The exact cause of PPD is not fully understood, but it’s believed to be a complex interplay of factors, including:
- Hormonal Changes: Dramatic shifts in hormone levels after childbirth can significantly impact mood.
- Sleep Deprivation: Lack of sleep, a common experience for new mothers, can exacerbate mood swings and worsen symptoms.
- Stress: Adjusting to a new baby, managing household responsibilities, and potential financial strain can contribute to stress levels.
- Social Isolation: Feeling isolated and lacking support can significantly impact mental well-being.
Risk Factors for Postpartum Depression
Certain factors can increase the risk of developing PPD, including:
- Previous Mental Health Issues: Women with a history of depression, anxiety, or other mental health conditions are at higher risk.
- Difficult Birth Experiences: A traumatic or complicated birth can increase the risk of PPD.
- Lack of Support: Limited support from partners, family, and friends can contribute to feelings of isolation and overwhelm.
- Financial Strain: Financial stress can exacerbate existing mental health challenges.

Seeking Help and Support
Recognizing the Need for Help
It’s important to understand that you are not alone in your struggle. Postpartum depression is a common experience, and seeking help is a sign of strength, not weakness. Pay attention to your emotions and behavior. If you are experiencing any of the symptoms mentioned above, don’t hesitate to reach out for support.
Building a Support Network
Talking openly with loved ones about your struggles is crucial. Sharing your feelings can help you feel less alone and can encourage loved ones to offer practical support. Consider joining support groups or online forums where you can connect with other mothers who understand what you’re going through.
Professional Help for Postpartum Depression
If you are struggling to cope with postpartum depression, seeking professional help is essential. A therapist, psychiatrist, or counselor can provide personalized treatment plans, medication management, and therapy skills to help you manage your symptoms.
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT helps you identify and challenge negative thoughts and behaviors that contribute to your depression.
- Interpersonal Therapy (IPT): IPT focuses on improving your relationships and communication skills to address interpersonal stressors that may be contributing to your depression.
Coping Strategies for Postpartum Depression
Self-Care: Prioritizing Your Well-being
Taking care of yourself is crucial for managing postpartum depression.
- Prioritize Sleep and Rest: Aim for at least 7-8 hours of sleep each night. If possible, nap during the day when your baby naps.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Focus on eating nutritious meals and staying hydrated.
- Exercise Regularly: Even moderate physical activity can boost your mood and energy levels.
- Practice Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga can help you manage stress and anxiety.
- Engage in Activities You Enjoy: Make time for activities that bring you joy and relaxation, even if it’s just for a few minutes each day.
Lifestyle Changes for Better Management
Making some lifestyle changes can also help you cope with postpartum depression.
- Establish a Routine: A structured daily routine can help reduce chaos and create a sense of normalcy.
- Seek Help with Childcare or Household Tasks: Don’t be afraid to ask for help with childcare or household chores. Allowing others to assist you can reduce your stress levels.
- Connect with Others: Spend time with loved ones, join a social group, or participate in activities that promote social interaction.
Parenting Support
Navigating the Challenges of Parenthood
Parenting is a challenging yet rewarding experience. It’s essential to remember that you are not alone in your journey.
- Seek Guidance from Parenting Professionals: Consider talking to a doula, lactation consultant, or other parenting professionals who can provide support and guidance.
- Utilize Parenting Resources: Join breastfeeding support groups, participate in online forums, or attend parenting classes to learn from other mothers and gain valuable information.
Resources and Support
Important Websites and Organizations
Several websites and organizations offer support and resources for mothers struggling with postpartum depression:
- Postpartum Support International (PSI): https://www.postpartum.net/
- The National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI): https://www.nami.org/
- The National Maternal Mental Health Hotline: https://mchb.hrsa.gov/
Seeking Professional Help
Remember, seeking professional help is a vital step in managing postpartum depression. Don’t hesitate to reach out to a therapist, psychiatrist, or counselor.
Finding Hope and Recovery
Understanding the Path to Recovery
Postpartum depression is treatable, and recovery is possible. With the right support and treatment, you can overcome this challenge and regain your well-being.
Building a Stronger Future
Sharing this information with others who may need it can help break the stigma surrounding postpartum depression. Encourage open communication and support for mothers experiencing these challenges. Remember, you are not alone, and there are resources available to help you on your journey to recovery.
Continue your journey of learning about animal care at *kienthucsannhi.com. We encourage you to interact with other readers by leaving comments, sharing this information, and exploring our wide range of articles. Let’s create a community where we can learn, grow, and support each other in our shared passion for animal well-being.*
FAQs
What are the signs of postpartum depression?
Postpartum depression can manifest in various ways, including emotional symptoms like feeling overwhelmed, sad, anxious, or inadequate as a parent; physical symptoms like fatigue, sleep disturbances, and changes in appetite; and behavioral symptoms like withdrawing from social interaction, neglecting personal hygiene, and difficulty concentrating.
How long does postpartum depression last?
Postpartum depression can last for weeks, months, or even years if left untreated. However, with proper treatment and support, most women experience significant improvement in their symptoms.
What are the best coping strategies for postpartum depression?
Effective coping strategies include prioritizing self-care by getting enough sleep, eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and practicing relaxation techniques. Seeking support from loved ones, joining support groups, and engaging in enjoyable activities can also help.
How can I find professional help for postpartum depression?
You can find professional help by contacting your primary care physician, a therapist, psychiatrist, or counselor. There are also online resources and hotlines that can connect you with mental health professionals in your area.
What are some resources for mothers struggling with postpartum depression?
Several websites and organizations provide support and resources for mothers experiencing postpartum depression, including Postpartum Support International (PSI), The National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI), and The National Maternal Mental Health Hotline.
EAVs
- Entity: Postpartum Depression | Attribute: Symptoms | Value: Mood Swings, Anxiety, Fatigue, Loss of Interest
- Entity: Postpartum Depression | Attribute: Causes | Value: Hormonal Changes, Sleep Deprivation, Stress
- Entity: Postpartum Depression | Attribute: Treatment | Value: Therapy, Medication, Support Groups
- Entity: Self-Care | Attribute: Strategies | Value: Exercise, Healthy Diet, Relaxation Techniques
- Entity: Support Network | Attribute: Sources | Value: Partner, Family, Friends, Support Groups
- Entity: Professional Help | Attribute: Specialists | Value: Therapists, Psychiatrists, Counselors
- Entity: Lifestyle Changes | Attribute: Examples | Value: Sleep Routine, Meal Planning, Exercise Schedule
- Entity: Parenting | Attribute: Challenges | Value: Sleep Deprivation, Feeding Difficulties, Emotional Demands
- Entity: Family | Attribute: Role | Value: Emotional Support, Practical Help, Childcare Assistance
- Entity: Community | Attribute: Resources | Value: Support Groups, Parenting Classes, Mental Health Services
- Entity: Postpartum Depression | Attribute: Severity | Value: Mild, Moderate, Severe
- Entity: Postpartum Depression | Attribute: Duration | Value: Few Weeks, Months, Years
- Entity: Symptoms | Attribute: Type | Value: Emotional, Physical, Behavioral
- Entity: Treatment | Attribute: Approach | Value: Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT), Interpersonal Therapy (IPT)
- Entity: Support Network | Attribute: Benefits | Value: Emotional Validation, Practical Help, Reduced Isolation
- Entity: Professional Help | Attribute: Benefits | Value: Personalized Treatment Plan, Medication Management, Therapy Skills
- Entity: Lifestyle Changes | Attribute: Benefits | Value: Reduced Stress, Improved Mood, Increased Energy
- Entity: Parenting | Attribute: Importance | Value: Bonding with Baby, Providing Safe and Nurturing Environment
- Entity: Family | Attribute: Importance | Value: Providing a Stable and Supportive Environment
- Entity: Community | Attribute: Importance | Value: Access to Resources and Support Networks
ERE
- Postpartum Depression – Is Caused By – Hormonal Changes
- Postpartum Depression – Can Be Treated By – Therapy
- Postpartum Depression – Is Supported By – Support Groups
- Postpartum Depression – Can Be Managed By – Self-Care
- Mothers – Experience – Postpartum Depression
- Mothers – Seek Support From – Family
- Mothers – Benefit From – Professional Help
- Therapists – Provide – Treatment for Postpartum Depression
- Medications – Can Help Manage – Postpartum Depression Symptoms
- Support Groups – Offer – Emotional Support and Practical Advice
- Self-Care – Involves – Prioritizing Sleep, Exercise, and Healthy Diet
- Lifestyle Changes – Include – Establishing Routine and Structure
- Parenting – Requires – Emotional and Physical Energy
- Family – Provides – Emotional Support and Practical Help
- Community – Offers – Resources and Support Networks
- Mothers – Benefit From – Parenting Classes
- Mothers – Benefit From – Mental Health Services
- Mothers – Benefit From – Childcare Assistance
- Postpartum Depression – Affects – Emotional Well-being
- Postpartum Depression – Affects – Ability to Care for Baby
Semantic Triples
- (Postpartum Depression, has symptom, mood swings)
- (Postpartum Depression, has symptom, anxiety)
- (Postpartum Depression, has cause, hormonal changes)
- (Postpartum Depression, can be treated with, therapy)
- (Postpartum Depression, can be treated with, medication)
- (Postpartum Depression, can be supported by, support groups)
- (Self-Care, includes, exercise)
- (Self-Care, includes, healthy diet)
- (Support Network, includes, partner)
- (Support Network, includes, family)
- (Professional Help, involves, therapist)
- (Lifestyle Changes, involves, sleep routine)
- (Parenting, involves, bonding with baby)
- (Family, provides, emotional support)
- (Community, provides, resources)
- (Mothers, experience, postpartum depression)
- (Mothers, seek, support from family)
- (Mothers, benefit from, professional help)
- (Therapists, provide, treatment for postpartum depression)
- (Medications, help manage, postpartum depression symptoms)